Firewall Log Forwarding
Using an external service to monitor the firewall enables you to receive alerts for important events, archived monitored information on systems with dedicated long-term storage, and integrate with third-party security monitoring tools.
Log storage on Palo Alto Networks firewalls is strictly allocated between different log and other storage types to ensure that no particular log is overrun by another. This allocation is user controlled.
Each storage area typically acts as circular logs in that, when filled, new entries will overwrite old ones. Space is cleared in blocks and messages added to the System log.
Before you can use Panorama or external systems to monitor the firewall, you must configure the firewall to forward its logs. Before forwarding to external services, the firewall automatically converts the logs to the necessary format: syslog messages, SNMP traps, or email notifications. Before you start this procedure, ensure that Panorama or the external server that will receive the log data already is set up.
External forwarding supports the following types of destinations:
1. SNMP traps
2. Syslog
3. Email
4. Panorama
There are two main methods to forward log events, depending on the log message type. Log events destined for the System, Config, and HIP Match log are redirected using Device > Log Settings to choose event destination (s) for specific event types.
Event normally written to the Traffic, Threat, and WildFire Submission logs are routed via a Log Forwarding profile.
Log forwarding profiles are attached to individual firewall Security policies to enable forwarding of the events associated with the processing of the specific policy. This granularity allows administrators specific control of forwarding and the potential of different forwarding for policies of differing importance.
All forwarded events are delivered as they are generated on the firewall.
A complete discussion of log forwarding configuration can be found on this link.
Syslog
I've used the free 3CDaemon Syslog server for my Palo Alto lab.
SNMP
I've used ManageEngine OpManager (v12.2), which is a free SNMP and NetFlow monitoring tool (up to 10 devices). You just need to allow the OpManager program on your personal firewall.
There's a warning saying that you need to allow OpManager to run on any installed Anti-virus and personal firewall settings.
It tool several minutes to complete the installation. You can login using the default username and password of admin/admin.
The OpManager wasn't able to detect the PAN firewall even though the SNMP Protocol Test Credential have Passed. I tried changing the OID to 1.3.6.1.6 and 1.3.6.1 (and changed Mask to 0xf0) but still SNMPv3 failed.
I tried configuring the SNMPv2c SNMP Community String (panfw200) instead.
The PAN firewall Status showed Trouble since its ethernet1/3 and ethernet1/4 are both down.
NetFlow
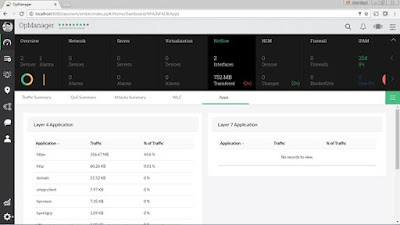
To view top talkers and top applications, go to Dashboard (gauge icon on the left-hand side) > click NetFlow column.
Using an external service to monitor the firewall enables you to receive alerts for important events, archived monitored information on systems with dedicated long-term storage, and integrate with third-party security monitoring tools.
Log storage on Palo Alto Networks firewalls is strictly allocated between different log and other storage types to ensure that no particular log is overrun by another. This allocation is user controlled.
Each storage area typically acts as circular logs in that, when filled, new entries will overwrite old ones. Space is cleared in blocks and messages added to the System log.
Before you can use Panorama or external systems to monitor the firewall, you must configure the firewall to forward its logs. Before forwarding to external services, the firewall automatically converts the logs to the necessary format: syslog messages, SNMP traps, or email notifications. Before you start this procedure, ensure that Panorama or the external server that will receive the log data already is set up.
External forwarding supports the following types of destinations:
1. SNMP traps
2. Syslog
3. Email
4. Panorama
There are two main methods to forward log events, depending on the log message type. Log events destined for the System, Config, and HIP Match log are redirected using Device > Log Settings to choose event destination (s) for specific event types.
Event normally written to the Traffic, Threat, and WildFire Submission logs are routed via a Log Forwarding profile.
Log forwarding profiles are attached to individual firewall Security policies to enable forwarding of the events associated with the processing of the specific policy. This granularity allows administrators specific control of forwarding and the potential of different forwarding for policies of differing importance.
All forwarded events are delivered as they are generated on the firewall.
A complete discussion of log forwarding configuration can be found on this link.
Syslog
I've used the free 3CDaemon Syslog server for my Palo Alto lab.
To configure a PAN firewall to send logs to an external Syslog
server, go to Device > Server Profiles
> Syslog > Add.
Type a Name for the
Syslog Server Profile (SYSLOG-PROF) > under Servers tab click Add > type
a Name for the server > type the IP address (or FQDN) under Syslog Server (10.67.78.3)
> leave the default settings for Transport, Port and Protocol columns >
choose LOG_LOCAL6 (Informational) under Facility > click OK.
As a best practice, network devices should be enabled for syslog facility level 6 (covers levels 0-6) under
normal operations. Level 7 is normally used for console troubleshooting (debug)
only.
To enable and forward Traffic and Threat logs to a Syslog
server (or to Panorama server), go to Objects
> Log Forwarding > Add.
Type a Name for the Log Forwarding Profile (LAB-FWD-PROF)
> under Traffic Settings click None under Syslog column > choose the
syslog profile created earlier (SYSLOG-PROF).
Choose the same syslog
profile (SYSLOG-PROF) under the Threat and WildFire Settings that you selected.
Click OK.
Apply the Log Forwarding Profile created on a Security
rule by going to Policies > Security.
I’ve enabled the Log Forwarding profile on Security rule 1 (ALLOW-PING) under Actions
tab > click Log at Session Start > choose LAB-FWD-PROF under Log
Forwarding.
I've also enabled Log Forwarding on Security rule 2
(ALLOW-INTERNET-ACCESS), which is my PAT rule from TRUST zone to
UNTRUST or Internet zone. Click Commit
to apply the changes.
As soon as the changes were applied, the PAN firewall
started sending syslogs. Notice the traffic
logs hit the rules such as the USER-INTERNET-ACCESS and ALLOW-PING.
SNMP
To configure SNMP on a PAN firewall, go to Device > Setup > Operations >
click SNMP Setup under Miscellaneous.
Type the Physical
Location and Contact > choose V3 under Version > under Name click Add to
create the SNMPv3 view profile.
Type a Name under View
(LAB-VIEW) > type the OID string 1.3.6.1.4.1.25461.2.3.12 (for PA-200) >
choose include under Options > type 0x80 under Mask > click OK.
Click Add under Users
to add the SNMPv3 user (panfw200) > choose LAB-VIEW under View > type
twice the Auth Password > type twice the Priv Password > click OK twice.
The PAN OS 7 (as of this writing) only supports SHA-1 (Authentication) and AES128
(Privacy) for SNMPv3.
To enable SNMP on the MGMT interface, go to Device > Setup > Management Interface
Settings > click Edit (gear icon).
Click SNMP under
Services > click OK > Commit.
I've used ManageEngine OpManager (v12.2), which is a free SNMP and NetFlow monitoring tool (up to 10 devices). You just need to allow the OpManager program on your personal firewall.
Just follow the steps on the installation wizard.
Choose Free
Edition in order to monitor up to 10 devices and the license will never
expire. This is good for a lab environment.
You can optionally choose other WebServer and
NetFlow ports. I've just changed the WebServer port to 8080 (since I’m running IIS on port 80) and left the NetFlow flow in default.
You can optionally fill up your personal information.
Wait until the installation completes.
Choose Standalone >
click Next.
Choose POSTGRESQL >
click Next.
There's a warning saying that you need to allow OpManager to run on any installed Anti-virus and personal firewall settings.
Click Finish and
OpManager (web client) will launch automatically (in a web browser).
It tool several minutes to complete the installation. You can login using the default username and password of admin/admin.
Press Esc to exit
the Youtube tour (opened in a new tab).
Go to Discovery >
Add Device > type the Device IP Address of the PAN firewall
(10.68.78.91/24).
Click Add Credential
on the right-hand side to configure SNMPv3 > choose Monitor under Credential
Category > choose SNMP v3 under Credential Type.
Type a Name of device
(PA-200-LAB) > optionally type a Description > type the SNMPv3 User Name
(panfw200).
Choose SHA (SHA-1)
under Authentication Protocol > type the Authentication password (configured
the same on the PAN firewall).
Choose AES-128 under
Encryption Protocol > type the Encryption (Privacy) password (configured the
same on the PAN firewall).
Leave the default SNMP
Port and timers in default > click Save.
The PA-200-LAB Credential will appear under Select all Credentials > select
PA-200-LAB > click OK.
The OpManager wasn't able to detect the PAN firewall even though the SNMP Protocol Test Credential have Passed. I tried changing the OID to 1.3.6.1.6 and 1.3.6.1 (and changed Mask to 0xf0) but still SNMPv3 failed.
I tried configuring the SNMPv2c SNMP Community String (panfw200) instead.
The PAN firewall Status showed Trouble since its ethernet1/3 and ethernet1/4 are both down.
Notice there are no interface bandwidth graphs since you need to
configure NetFlow in order to view interface traffic and
top talkers on the network.
NetFlow
To configure NetFlow on a PAN firewall, go to Device >
Server Profiles > NetFlow > Add.
Type a Name of the NetFlow Profile (NETFLOW-PROF) > click
Add under Name > type a Name for the server (SERVER-1) > type the NetFlow
Server IP address (10.67.78.3) > change the port to 9996 (used by OpManager)
> click OK.
Apply the NetFlow Profile on the PAN firewall interfaces that you
want to monitor. You usually enable NetFlow on the ingress (ethernet1/2 or
TRUST-L3) and egress (ethernet1/1 or UNTRUST-L3) interfaces. Go to Network >
Interfaces.
Click on the interface (ethernet1/1) > choose the NetFlow
profile created earlier (NETFLOW-PROF) under NetFlow Profile > click OK.
Configure the same on the ingress interfaces (ethernet1/2). Click Commit afterwards.
The interface bandwidths graphs were generated after NetFlow
(see Version 9 under Flow Analysis) was enabled on the ingress (ethernet1/2) and
egress (ethernet1/1) interfaces on the PAN firewall.
These are the bandwidth graphs for the ingress (ethernet1/2)
interface.
To view top talkers and top applications, go to Dashboard (gauge icon on the left-hand side) > click NetFlow column.

























































































No comments:
Post a Comment